APPSC AE Syllabus 2021 PDF | Check Exam Pattern Details Now: The officials of the Andhra Pradesh Public Service Commission have released the syllabus and exam pattern for the Assistant Engineer Post. Aspirants who have all applied for the written exam now wanted to prepare for their examination. All those candidates now refer to the syllabus and exam pattern through this article. By knowing the syllabus candidates can have an idea of preparation for the written examination. The selection to this recruitment notification will be based on the Merit in the Written Exam to be held as per the Scheme and Syllabus.
APPSC AE Syllabus 2021 – Complete Details
| Check APPSC AE Syllabus 2021 PDF @ psc.ap.gov.in | |
| Organization | Andhra Pradesh Public Service Commission (APPSC) |
| Post Name | Assistant Engineer (AE) |
| Syllabus Status | Available Now |
| Category | Syllabus |
| Official Site | https://psc.ap.gov.in/ |
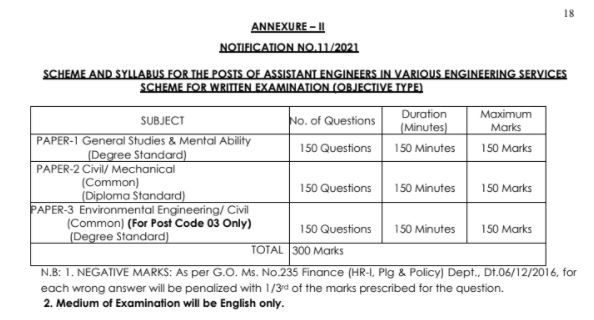
APPSC AE Exam Pattern 2021
| SUBJECT | No. of Questions | Duration (Minutes) | Maximum Marks |
| PAPER-1 General Studies & Mental Ability (Degree Standard) | 150 Questions | 150 Minutes | 150 Minutes |
| PAPER-2 Civil/ Mechanical (Common) (Diploma Standard) | 150 Questions | 150 Minutes | 150 Minutes |
| PAPER-3 Environmental Engineering/ Civil (Common) (For Post Code 03 Only) (Degree Standard) | 150 Questions | 150 Minutes | 150 Minutes |
| Total | 300 Marks | ||
APPSC Assistant Engineer Syllabus 2021 PDF
Paper –I: General Studies & Mental Ability
- Events of national and international importance.
- Current affairs- international, national, and regional.
- General Science and its applications to the day to day life Contemporary developments in Science & Technology and Information Technology
- The social-economic and political history of modern India with emphasis on Andhra Pradesh.
- Indian polity and governance: constitutional issues, public policy, reforms and e-governance initiatives with specific reference to Andhra Pradesh.
- Economic development in India since independence with emphasis on Andhra Pradesh.
- Physical geography of Indian sub-continent and Andhra Pradesh.
- Disaster management: vulnerability profile, prevention and mitigation strategies, Application of Remote Sensing and GIS in the assessment of Disaster.
- Sustainable Development and Environmental Protection
- Logical reasoning, analytical ability, and data interpretation.
- Data Analysis: a) Tabulation of data b) Visual representation of data c) Basic data analysis (Summary Statistics such as mean, median, mode, variance, and coefficient of variation) and Interpretation
- Bifurcation of Andhra Pradesh and its Administrative, Economic, Social, Cultural, Political, and Legal implications/problems.
Paper-2 (Common for Civil / Mechanical)
Solid Mechanics:
- Forces: Different types of forces, gravitational, frictional, axial, tensile, or compressive. Law of Parallelogram and triangle of forces, a polygon of forces, problems.
- Centre of gravity and moment of inertia. Simple plane figures, Simple machines, the law of machine, Mechanical advantage, velocity ratio and efficiency, wheel and axle, pulleys, and simple screw jack problems.
- Simple Stresses and strains: Different types of stresses and strains, stress-strain diagram for ductile materials. The factor of safety, ultimate strength, and working strength, elastic constants, Poisson ratio. Deformations, volume changes. Relations between elastic constants. Hooke’s Law. Compound rods, temperature stresses, strain energy, impact loading.
- Riveted and welded joints, different modes of failures, the efficiency of joints, thin cylindrical shells, longitudinal and circumferential stresses, and volume changes.
- Shear force and bending moment diagrams for simply supported, overhanging, and cantilever beams. Relation between the intensity of loading, shear force, and bending moment.
- Theory of simple bending: Assumptions, basic flexure formula, bending stresses, modulus of the section, a moment of resistance. Circular bending. Distribution of shear stress in common structural sections.
- Deflection in cantilever and simply supported beams under simple loading- propped cantilever beams subjected to simple loading, determination of reaction. SF and BM diagrams.
- Simple plane and pin-jointed trusses: Stresses by the method of joints and method of sections.
- Torsion: Assumptions, the basic formula of torsion, power transmission by shafts of uniform circular sections close-coiled springs, strain-energy in simple beams and shafts, sudden and impact loading. Principal stresses and principal planes. Moher’s circle of stress.
- Thin cylinders under internal pressure stresses and volume changes.
- Columns and struts: Direct and bending stresses, the core of section. Short and long columns under axial loading-various end conditions. Euler and Rankine formulae, Slenderness ratio, simple built-up columns.
Fluid Mechanics:
- Introduction: Scope of hydraulics in Engineering. Definition and properties of the fluid.
- Fluid pressure and its measurement: Atmospheric pressure, Gauge pressure, and absolute pressure. Piezometer, Manometer-U-tube, Inverted U-tube, and differential manometers.
- Pressure on plane surface immersed in a liquid-Horizontal, vertical, and inclined plane surface.
- The flow of fluids: Type of flow-uniform flow, non-uniform flow, streamline flow, Turbulent flow, steady flow, and unsteady flow, Energies in fluid motion-Datum head, pressure head, and velocity head. The total energy of the fluid in motion – Bernoulli’s theorem. Practical application of Bernoulli’s theorem – flow measurement- pitot tube venturi meter – Orifice meter.
- Flow-through orifices and Mouth Pieces: Definition of the orifice, types of orifices, Vena contracta, coefficient of velocity, coefficient of contraction, coefficient of discharge. Submerged and partially submerged orifices. Flow-through orifices
- under variable heads – Time of emptying a rectangular tank through orifices. Mouthpieces – different types of problems.
- Notches and Weirs: Definition of the notch, types of notches – Rectangular notch, Triangular notch, and trapezoidal notch. Discharge over rectangular, triangular, and trapezoidal notches.
- Flow-through pipes: Major and minor losses – Loss of head at the entrance, loss of head due to sudden enlargement, due to sudden contraction, loss of head at the exit of the pipe. Frictional loss in pipe-Chezy formula and Darcy’s formula. ix) Hydraulic gradient and total energy line. Discharge through parallel pipes and branched pipes connected to a reservoir. Flow-through siphon pipe.
Paper-3 (Common for Environmental/ Civil):
1.Water Supply Engineering Sources of water: surface and sub-surface water, aquifers, yield from wells, Infiltration galleries, types of intakes and design of intakes, collection and conveyance of water; water demand and it’s variations, estimation of water demand; quality of water, characteristics, water-borne diseases, water sampling and analysis, water quality standards; Water Treatment: unit operations and processes for water treatment, sedimentation, coagulation and flocculation, filtration, disinfection, water softening, removal of colour, iron and manganese; aeration, Defluoridation of water, demineralisation of water, R.O. process, principles and design of various water treatment units; Distribution of treated water, systems of water distribution, layouts of distribution systems, components of distribution systems, valves, analysis and design of the water distribution systems, Storage and distribution reservoirs; leakages and control in water distribution system; Rural water supply;
2. Wastewater Engineering Systems of sewage collection, conveyance, and disposal; estimation of the quantity of sewage and stormwater, sewerage systems, sewer appurtenances, material for sewers, laying of sewers, Design of sewers, operation and maintenance of sewerage systems; pumping of sewage; Characteristics of sewage, sampling, and analysis of sewage, unit operations and process for wastewater treatment, aerobic, anaerobic, facultative and anoxic processes, principles and design of various wastewater treatment units, principles and design of septic tanks, disposal of septic tank effluent; Common Effluent Treatment Plants, Zero liquid discharge; Disposal of products of sewage treatment; Sludge handling, treatment, and disposal; self-purification of streams; Building drainage, Plumbing Systems; Rural and semi-urban sanitation; Urban stormwater management, Impact of stormwater, Management of stormwater runoff, design of stormwater drainage systems;
3. Solid Waste Management Sources of solid waste, classification, characteristics, generation, on-site segregation and storage, collection, transfer, and transportation of solid waste; principles and engineering systems for solid waste management, treatment, and processing of solid waste; landfills and their classification, principles, design, and management of landfills; Leachate management, disposal of solid waste; Hazardous waste characteristics, handling, storage, collection and transportation, treatment and disposal; e-waste: sources, collection, treatment, and reuse;
- Water Resources Engineering
- i) Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machines Physical properties of fluids, fluid statics; fluid flow concepts, Kinematics of flow, continuity, momentum and energy principles and corresponding equations; Flow measurement; dimensional analysis and hydraulic similitude; flow through pipes and open channel hydraulics; Hydraulic jump, Surges, and Water hammer; Basic principles of hydraulic machines, turbines and pumps, types, selection, performance parameters, controls, scaling, pumps in parallel; Hydraulic ram;
- ii) Hydrology Hydrological cycle, precipitation and its estimation, evaporation and transpiration, runoff estimation; hydrographs; Floods estimation and routing, flood management; Streams and their gauging; capacity of Reservoirs. Watershed management and rainwater harvesting; groundwater hydrology: steady-state well hydraulics and application of Darcy’s law, recuperation test for good yield, groundwater management;
iii) Irrigation Water resources of the earth, irrigation systems, advantages and disadvantages of irrigation, duty, delta, crop water requirements; Water logging and drainage, Design of canals, headworks, canal distribution works, falls, cross drainage works, canal lining; Sediment transport in canals;
- Surveying Principles of surveying, classification of surveys; Measurement of distances and directions, direct and indirect methods; optical and electronic devices; chain and compass survey; leveling and trigonometric leveling, Contours; Theodolite and tachometric survey; Total station, triangulations and traversing; measurements and adjustment of observations, errors and their adjustments, computation of coordinates; minor instruments; area and volumes; curve setting, horizontal and vertical curves; Digital elevation modeling concept; basic concepts of remote sensing, GIS and global positioning system;
- Soil Mechanics And Foundation Engineering Physical and index properties of soil, classification and interrelationship; Permeability and seepage, Darcy’s law; flow nets, uplift pressure, piping; Compressibility and consolidation; Compaction behavior, methods of compaction and their choice; Shear strength of soils, stresses, and failure, Mohr’s circle; Earth pressure theories, stability analysis of slopes, retaining structures, stress distribution in soil; site investigations and sub-surface exploration; Types of foundations, selection criteria, bearing capacity, the effect of the water table, settlement, laboratory and field tests; principles and design considerations of shallow and deep foundations; Types of piles, their design and layout, pile load tests, Caissons, Foundations on expansive soils, swelling and its prevention;
- Transportation Engineering Planning and development of highway, classification of roads, highway alignment, and geometric design, cross-sectional elements, sight distance, horizontal and vertical alignment, grade separation; Highway materials, their properties, and quality tests, construction of earthen, W.B.M., Bitumen and cement concrete roads; bitumen mix design; Maintenance of all types of roads, disposal of muck, highway drainage, Street lighting; design of flexible and rigid pavements using IRC recommendations; Traffic engineering, traffic characteristics, traffic surveys, traffic control devices, intersections, signaling; Mass transit systems, accessibility, traffic control, emergency management. Airports, layout and orientation, site selection; runway and taxiway design; drainage management; Zoning laws; Helipads, Airport obstructions, Visual aids, and air traffic control;
- Solid Mechanics and Analysis Of Structures
- i) Solid Mechanics
Simple stress and strain relationships, Bending moment flexural and shear stresses in statically determinate beams; Elastic theories of failure; Torsion of circular and rectangular sections and simple members; buckling of column, combined and direct bending stresses.
- ii) Structural Analysis
Analysis of statically determinate and indeterminate structures by force/ energy methods; Method of superposition; Analysis of trusses, arches, beams, cables, and frames; Analysis of thin and thick cylinders; Slope deflection, moment distribution, and Stiffness and flexibility methods of structural analysis; Influence lines;
- Design Of Structures
- i) Reinforced Concrete Structures Concepts of working stress, limit state, and ultimate load design methods; IS code specifications for the design of beams, slabs, columns, footings, and walls; design of beams, slabs, columns; Analysis of beam sections at transfer and service loads; Design of wall footings, foundations, retaining walls, and water tanks Principles of prestressed concrete, methods of prestressing; design of simple members; Design of brick masonry
- ii) Steel Structures Concepts of Working stress and Limit state design methods; Design of tension and compression members, beams, columns, and column bases; Connections – simple and eccentric, beam-column connections, plate girders and trusses;
- Building Materials and Construction Practice Building Materials: composition and properties of timber, bricks, cement, concrete, structural steel, plywood; mix design, short-term and long-term properties of concrete and mortar; Bitumen; Brick masonry, the influence of mortar strength on masonry strength. Importance of W/C Ratio, Strength, ingredients including admixtures, workability, testing for strength, elasticity, nondestructive testing, mix design methods in concrete; Green building concepts Construction Management: Types of construction projects; Concreting Equipment, Earthwork Equipment, Tendering and construction contracts; Rate analysis and standard specifications; Cost estimation; Project planning and network analysis: PERT and CPM, Resource allocation.
Download APPSC AE Syllabus 2021 (Available Now) ![]()

