BITSAT Syllabus 2021 PDF | Download Exam Pattern Here: Birla Institute of Science and Technology Admission Test (BITSAT) officials have released for Admission Test (BITSAT) – 2021. BITSAT Exam Pattern & Syllabus 2021 has been uploaded now at www.bitsadmission.com. Further, Candidates who have applied in this recruitment 2021. And stay in touch with his article to get details regarding Syllabus, Exam Pattern, Exam Date details. For ease of access, We have also attached the direct download link below.
BITSAT Syllabus 2021 – Overview
| BITSAT Syllabus 2021 PDF @ www.bitsadmission.com | |
| Organization | Birla Institute of Science and Technology Admission Test (BITSAT |
| Post Name | Admission Test (BITSAT) – 2021 |
| Category | Syllabus |
| Official Site | www.bitsadmission.com |
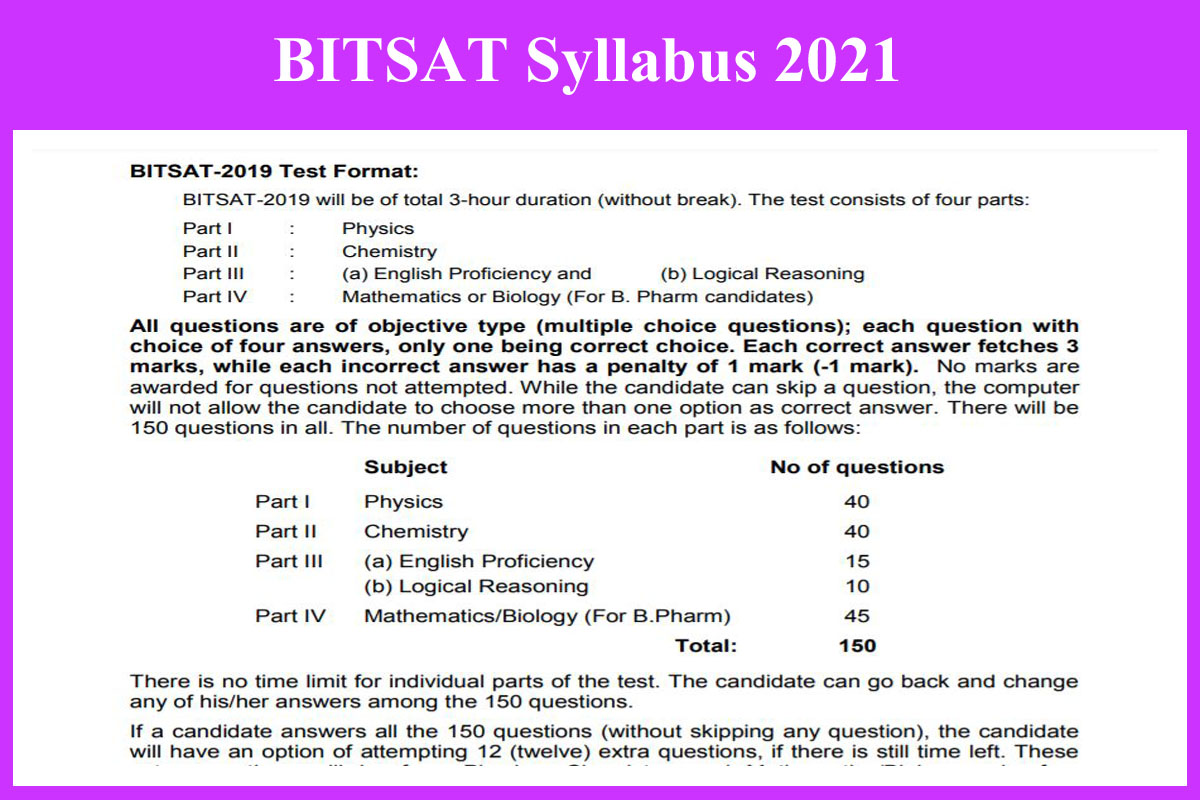
BITSAT Exam Pattern 2021:-
| Part | Type of Test | Subject | No. of Questions | Duration |
| Part I | Objective Type (multiple choice questions) | Physics | 40 | 3 Hours |
| Part II | Chemistry | 40 | ||
| Part III | English Proficiency | 15 | ||
| Logical Reasoning | 10 | |||
| Part IV | Mathematics/Biology (For B. Pharm) | 45 | ||
| Total | 150 | |||
BITSAT Syllabus 2021:-
Part I: Physics
1. Units & Measurement
- Units (Different systems of units, SI units, fundamental and derived units)
- Dimensional Analysis
- Precision and significant figures
- Fundamental measurements in Physics (Vernier calipers, screw gauge, Physical balance etc)
2. Kinematics
- Properties of vectors
- Position, velocity and acceleration vectors
- Motion with constant acceleration
- Projectile motion
- Uniform circular motion
- Relative motion
3. Newton’s Laws of Motion
- Newton’s laws (free body diagram, resolution of forces)
- Motion on an inclined plane
- The motion of blocks with pulley systems
- Circular motion – centripetal force
- Inertial and non-inertial frames
4. Impulse and Momentum
- Definition of impulse and momentum
- Conservation of momentum
- Collisions
- The momentum of a system of particles
- 4.5 Center of mass
5. Work and Energy
- Work done by a force
- Kinetic energy and work-energy theorem
- Power
- Conservative forces and potential energy
- Conservation of mechanical energy
6. Rotational Motion
- Description of rotation (angular displacement, angular velocity and angular acceleration)
- Rotational motion with constant angular acceleration
- Moment of inertia, Parallel and perpendicular axes theorems, rotational kinetic energy
- Torque and angular momentum
- Conservation of angular momentum
- Rolling motion
7. Gravitation
- Newton’s law of gravitation
- Gravitational potential energy, Escape velocity
- The motion of planets – Kepler’s laws, satellite motion
8. Mechanics of Solids and Fluids
- Elasticity
- Pressure, density and Archimedes’ principle
- Viscosity and Surface Tension
- Bernoulli’s theorem
9. Oscillations
- Kinematics of simple harmonic motion
- Spring mass system, simple and compound pendulum
- Forced & damped oscillations, resonance
10. Waves
10.1 Progressive sinusoidal waves
10.2 Standing waves in strings and pipes
10.3 Superposition of waves, beats
10.4 Doppler Effect
11. Heat and Thermodynamics
11.1 Kinetic theory of gases
11.2 Thermal equilibrium and temperature
11.3 Specific heat, Heat Transfer – Conduction, convection and radiation, thermal conductivity, Newton’s
law of cooling
XIII
11.4 Work, heat and the first law of thermodynamics
11.5 2
nd
law of thermodynamics, Carnot engine – Efficiency and Coefficient of performance
12. Electrostatics
12.1 Coulomb’s law
12.2 Electric field (discrete and continuous charge distributions)
12.3 Electrostatic potential and Electrostatic potential energy
12.4 Gauss’ law and its applications
12.5 Electric dipole
12.6 Capacitance and dielectrics (parallel plate capacitor, capacitors in series and parallel)
13. Current Electricity
13.1 Ohm’s law, Joule heating
13.2 D.C circuits – Resistors and cells in series and parallel, Kirchoff’s laws, potentiometer, and Wheatstone
bridge
13.3 Electrical Resistance (Resistivity, origin, and temperature dependence of resistivity).
14. Magnetic Effect of Current
14.1 Biot-Savart’s law and its applications
14.2 Ampere’s law and its applications
14.3 Lorentz force, force on current-carrying conductors in a magnetic field
14.4 Magnetic moment of a current loop, torque on a current loop, Galvanometer and its conversion to
voltmeter and ammeter
15. Electromagnetic Induction
15.1 Faraday’s law, Lenz’s law, eddy currents
15.2 Self and mutual inductance
15.3 Transformers and generators
15.4 Alternating current (peak and RMS value)
15.5 AC circuits, LCR circuits
16. Optics
16.1 Laws of reflection and refraction
16.2 Lenses and mirrors
16.3 Optical instruments – telescope and microscope
16.4 Interference – Huygen’s principle, Young’s double-slit experiment
16.5 Interference in thin films
16.6 Diffraction due to a single slit
16.7 Electromagnetic waves and their characteristics (only qualitative ideas), Electromagnetic spectrum
16.8 Polarization – states of polarization, Malus’ law, Brewster’s law
17. Modern Physics
17.1 Dual nature of light and matter – Photoelectric effect, De Broglie wavelength
17.2 Atomic models – Rutherford’s experiment, Bohr’s atomic model
XIV
17.3 Hydrogen atom spectrum
17.4 Radioactivity
17.5 Nuclear reactions: Fission and fusion, binding energy
18. Electronic Devices
18.1 Energy bands in solids (qualitative ideas only), conductors, insulators, and semiconductors;
18.2 Semiconductor diode – I-V characteristics in forward and reverse bias, diode as a rectifier; I-V
characteristics of LED, photodiode, solar cell, and Zener diode; Zener diode as a voltage regulator.
18.3 Junction transistor, transistor action, characteristics of a transistor; transistor as an amplifier (common
emitter configuration) and oscillator
18.4 Logic gates (OR, AND, NOT, NAND and NOR).
Download BITSAT Syllabus 2021 PDF

