GPSC Assistant Professor Syllabus 2021 Out | Download Now: The officials of Gujarat Public Service Commission has released the Syllabus and Exam Pattern for Professor, Associate Professor & Assistant Professor Post. As of now candidates can prepare the GPSC Assistant Professor Exam from here. So that applicants can easily get an idea of preparing the examination. So all the aspirants are advised to read this article entirely and do their exams well.
GPSC Assistant Professor Syllabus 2021 – Details
| Download GPSC Assistant Professor 2021 Syllabus PDF @ gpsc.gujarat.gov.in | |
| Organization | Gujarat Public Service Commission |
| Post Name | Professor, Associate Professor & Assistant Professor |
| Exam Dates | Announce Soon |
| Status | Available Now |
| Category | Syllabus |
| Official Site | gpsc.gujarat.gov.in |
GPSC Assistant Professor Exam Pattern 2021
| Type of Questions | Marks | Medium |
| Basic Science | 200 | English |
| Concerned Subjects | ||
| No of Questions | 200 | |
GPSC Assistant Professor Syllabus 2021
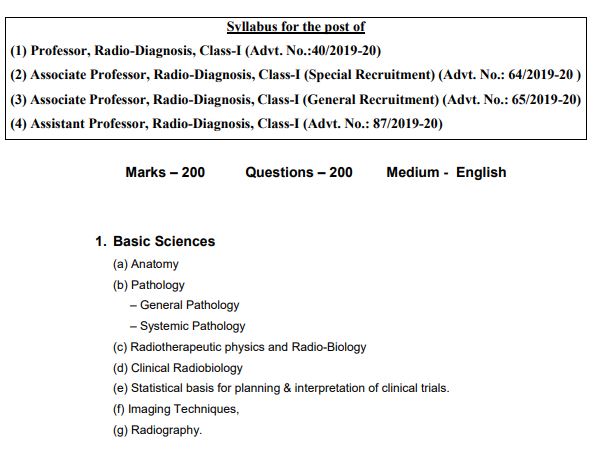
Professor, Radio-Diagnosis, Class-I. Associate Professor, Radio-Diagnosis, Class-I .Assistant Professor, Radio-Diagnosis, Class-I
-
Basic Sciences
(a) Anatomy
(b) Pathology
– General Pathology
– Systemic Pathology
(c) Radiotherapeutic physics and Radio-Biology
(d) Clinical Radiobiology
(e) Statistical basis for planning & interpretation of clinical trials.
(f) Imaging Techniques,
(g) Radiography.
2. BASIC SCIENCES RELATED TO RADIO-DIAGNOSIS
Radiation physics and Radio-Biology – Radiological anatomy and pathology of various organ systems – Imaging Techniques – Radiography. Includes all aspects of: Fundamentals of electromagnetic radiation, X-Ray production, characteristic properties of X-Rays, units of radiation, radiation measurement, X-ray equipment’s, X-Ray films, intensifying screens, other X-Ray appliances, dark room equipment’s and procedures, II TV, cine fluorography, tomography.
- Quality assurance
- Radiation hazards and principle and methods of radiation protection
- Contrast media: types, chemistry, mechanisms of action, dose schedule, routes of administration, their potential adverse reactions and management.
- Clinical applications of important isotopes and instrumentation in Nuclear medicine with advances in both.
- Physics and applications of advanced imaging i.e., Ultrasound, CT, MRI, Angiography (DSA), PET etc.
- Practical experiments in physics : A list of experiments, which a resident should be able to do and interpret the results, is available in the department.
3. Radiological Physics
Introduction of general properties of radiation and matter: Fundamentals of nuclear physics and radioactivity – Interaction of x-rays and gamma rays with matter and their effects on irradiated materials – X-ray Generating Apparatus – Screen-film radiography – Film processing: Dark room, dry processing, laser/dry chemistry cameras, artifacts – Fluoroscopy: Digital including flat panel units, fluoroscopy cum radiography units – Digital radiography: Computed Radiography, Flat panel radiography – Other equipment’s: Ultrasound including Doppler, CT, MRI and DSA – Contrast Media (Iodinated, MR & Ultrasound) – types, chemical composition, mechanism of action, dose schedule, route of
administration, adverse reaction and their management – Nuclear Medicine: Equipment’s and isotopes in various organ systems and recent advances – Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS) and Radiology Information System (RIS) to make a film-less department and for Tele radiology – Radiation protection, dosimetry and radiation biology – Image quality and Quality Assurance (QA) – Recent advances in radiology and imaging.
4. Radiography and processing techniques
Processing techniques: includes dark room and dry processing – Radiography of the musculo-skeletal system including extremities – Radiography of the chest, spine, abdomen and pelvic girdle – Radiography of the skull, orbit, sinuses – Contrast techniques and interpretation of GI tract, hepato-biliary tract, pancreas etc.- Contrast techniques and interpretation of the Central Nervous system. – Contrast techniques and interpretation of the cardiovascular system including chest – Contrast techniques and interpretation of the genito – urinary system including Obstetrics and Gynaecology – Paediatric radiology including MCU, genitogram, bone age. – Dental, portable and emergency (casualty)
radiography.
5. Radio-Diagnosis Theory Study
- Basic sciences related to Radiology (consists of Anatomy, Pathology, Basic and Radiation Physics, Imaging Techniques, and Film processing)
- Chest, CVS, CNS including Head & Neck, Eye, ENT, musculo-skeletal, pediatric radiology and Mammography
- Abdominal Imaging including GI, GU, Hepatobiliary, endocrine and metabolic, Obstetrics and Gynaecology and Interventional radiology
- Recent advances, nuclear medicine; Radiology related to clinical specialties advances, nuclear medicine; Radiology related to clinical specialties
6. RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
Diseases of the chest wall, diaphragm, pleura and airways; pulmonary infections; pulmonary vasculature; pulmonary neoplasms; diffuse lung disease; mediastinal disease; chest trauma; post- operative lung and X-Rays in intensive care.
7. GASTROINTESTINAL (GIT) AND HEPATO-BILIARYPANCREATIC SYSTEM
Diseases and disorders of mouth, pharynx, salivary glands, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, diseases of omentum, peritoneum and mesentery, acute abdomen, abdominal trauma using conventional and newer imaging methods like CT, MRI, DSA, isotope studies. Diseases and disorders of hepato-biliary-pancreatic system using conventional & newer imaging methods.
8. GENITO-URINARY SYSTEM
Imaging: conventional, ultrasound, CT, MRI, angiography; of various diseases and disorders of genitourinary system. These includes: congenital, inflammatory, traumatic, neoplastic, calculus and miscellaneous conditions.
9. MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM
Imaging (Conventional, ultrasound, CT, MRI, angiography, Radio-isotope studies) and interpretation of diseases of muscles, soft tissue, bones and joints including congenital, inflammatory, traumatic, neoplastic and miscellaneous conditions.
10. CARDIOVASCULAR RADIOLOGY/ECHO CARDIOGRAPHY
Diseases and disorders of cardiovascular system including congenital conditions and the role of imaging by conventional, ultrasound, Echo, color Doppler, CT, MRI, angiography (including DSA) and radionuclide studies. It also includes interventional procedures e.g; balloon angioplaty, embolization, etc.
11. NEURORADIOLOGY
Includes imaging (using conventional and newer methods) and interpretation of various diseases and disorders of the head, neck and spine covering congenital lesions, infective lesions, vascular lesions, traumatic conditions and neoplasia. It also includes a number of interventional procedures carried out in the department of neuroradiology.
12. ULTRASOUND (INCLUDING GYNAE/OBSTETRICS)
Interpret all ultrasound studies. These studies include : abdomen, pelvis, small parts, neonatal head, color-duplex imaging (including peripheral i.e; extremity arterial and venous studies), obstetrics/gynaecology (in the deptt of Gyn/Obstet) and interventional procedures using ultrasound guidance. The resident should have a thorough knowledge of the common abnormalities of the abdominal/pelvic organs, retroperitoneal structures, neck, chest, extremities and small parts (thyroid/parathyroid, scrotum, orbit, breast).
13. PAEDIATRIC RADIOLOGY
Common diseases and disorders of different organ systems covering congenital, inflammatory, traumatic, neoplastic and other miscellaneous conditions, using both conventional and newer imaging methods.
14. GENERAL RADIOLGY
15. CT
16. ANGIOGRAPHY AND INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGY
17. RADIOLOGY IN EMERGENCY MEDICINE
18. ONCOLOGIC RADIOLOGY
19. NUCLEAR MEDICINE
20. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY.
21. MEDICO LEGAL ASPECTS RELEVANT TO THE DISCIPLINE.
22. INDIAN MEDICAL COUNCIL (PROFESSIONAL CONDUCT,
ETIQUETTE AND ETHICS) REGULATIONS, 2002.
23. CURRENT TRENDS AND RECENT ADVANCEMENTS IN THE
FIELD OF RADIO-DIAGNOSIS
Professor, Biochemistry, Class-I, Associate Professor, Biochemistry, Class-I, Assistant Professor, Biochemistry, Class-I:
1.BIOMOLECULES:
Properties of water, Concept of an acid, a base, pH, pK, buffer and buffering capacity; Classification, structure and functions of amino acids and peptides; Structural organization of proteins and relationship with their functions, Structure-function relationship of proteins; Classification, functions, properties and reactions of carbohydrates; Classification, properties and importance of lipids; nucleotides and nucleic acids.
2. CELL BIOLOGY
Structure of the cell and different subcellular organelles, Structure and functions of cell membrane, solute transport across biological Membranes, Interaction between cells and environment, Glycoprotein’s and proteoglycans, Intracellular traffic and sorting of proteins, endoplasmic reticulum, Intracellular signaling pathways, membrane receptors and second messengers, Extracellular matrix: composition, importance and biomedical importance,
cellular adhesion molecules and intercellular communication, Cytoskeleton, muscle contraction and cell motility, Cell cycle, mitosis, meiosis and mechanisms of cell death, Red and white blood cells
3. ANALYTICAL TECHNIQUES IN BIOCHEMISTRY
Spectrophotometry (UV and visible spectrophotometry), atomic absorption spectrophotometry, Flame photometry, Fluorometry, Turbidimetry and nephelometry, Gravimetry, Electrochemistry (pH electrodes, ion-selective electrodes, gas-sensing electrodes), Chemiluminescence, Water testing, Electrophoresis (principle, types, applications; isoelectric focusing capillary electrophoresis; 2-D electrophoresis), Chromatography (principle, types [including high performance liquid chromatography and gas chromatography], Techniques in molecular biology: Blotting techniques, polymerase chain reaction (PCR), DNA and protein sequencing, microarrays and DNA chip
technology, cloning techniques, genomics, proteomics and metabolomics.
4. Nanotechnology and microfabrication
5. Radioisotope-based techniques and its application
6. Biostatistics and research methodology
7. ENZYMES, BIOLOGICAL OXIDATION, RESPIRATORY CHAIN AND OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATIONS
- ENZYMES: Properties, classification, mechanism of action, coenzymes and cofactors, kinetics of enzyme activity, regulation of enzyme activity, isoenzymes, diagnostic and therapeutic enzymes, principles of assays of enzymes, enzymes as therapeutic targets of drugs,
- Biological oxidation: Basic concepts of thermodynamics and its laws, as applied to living systems, Exergonic and endergonic reactions and coupled reactions, redox potential, High energy compounds, Classification and role of oxidoreductases, Cytochromes; cytochrome P450 system
- Respiratory chain and oxidative phosphorylation: Components, complexes and functioning of the respiratory chain, Process of oxidative phosphorylation Mechanisms of ATP synthesis and regulation, Mitochondrial transport systems and shuttles, Inhibitors, uncouplers and ionophores, OXPHOS diseases.
8. Overview of Metabolism and Intermediary Metabolism:
- Metabolism of carbohydrates,
- Metabolism of lipids,
- Metabolism of amino acids and Proteins,
- Metabolism of nucleotides,
- Metabolism of haem,
- Metabolism in individual tissues and in the fed and fasting states
9. NUTRITION, VITAMINS, MINERALS
- Nutrition: Principal food components, General nutritional requirements, Energy requirements Biological value of proteins, Thermogenic effect of food, Balanced diet, diet formulations in health and disease, mixed diet, Nutritional supplements, Food toxins and additives, Parenteral nutrition, Disorders of nutrition, obesity, protein and protein energy malnutrition, dietary fibers, under-nutrition, laboratory diagnosis of nutritional disorders, National Nutrition Programme.
- Vitamins: Classification, biochemical role, sources, RDA and deficiency state of each vitamin, (including diagnostic tests for deficiency and treatment)
- Minerals: Classification, biochemical role, sources, requirement and deficiency state of each mineral, (including diagnostic tests for deficiency and treatment).
10. MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
Structure and organization of chromosomes and chromatin re-modelling: DNA replication, Transcription, Genetic code and mutations, Translation, Regulation of gene expression in prokaryotes and eukaryotes, Recombinant DNA technology and its applications in modern medicine
11. Basics of Bioinformatics
- Principles of Human Genetics: Alleles, genotypes and phenotypes, Patterns of inheritance: monogenic and polygenic inheritance, Population genetics, Genetic factors in causation of diseases, Types of genetic diseases: Chromosomal, monogenic and polygenic disorders, mitochondrial disorders, nucleotide repeat expansion disorders, imprinting disorders; Screening for genetic diseases and prenatal testing, Ethical and legal issues related to medical genetics
- Stem cells in clinical medicine: Basic concepts regarding stem cells, Types of stem cells: embryonic and induced pleuripotent stem cells (IPSC), Potential applications in the clinical medicine, Ethical and legal issues related to use of stem cells in medicine
- Cancer: Carcinogens: physical, chemical and biological, Clonal origin of cancers, Genetic basis of carcinogenesis, Role of oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes, Familial cancer syndromes, Cancer stem cells, Epigenetic regulation in cancer, Gene expression profiling in cancer, Cancer cell biology: cell cycle abnormalities, telomerase activity, proliferative capacity and decreased apoptosis, Metastasis, Tumor markers, Biochemical basis of cancer chemotherapy and drug resistance, New methods of anti-cancer therapy:
targeted cancer therapy, cancer immunotherapy.
12. Immunology
Innate and acquired immunity, Humoral and cell-mediated immunity, Cells and organs of the immune system – T and B cells, macrophages, dendritic cells, NK cells, granulocyte, Antigens, epitopes and haptens, Immunoglobulin classes, isotypes, allotypes, idiotypes, monoclonal antibodies, organization and expression of immunoglobulin genes, immunoglobulin gene rearrangement, class switching, Antigen-antibody interaction – immunochemical techniques, Major histocompatibility complex, antigen processing and presentation, T cell and B cell receptor, toll like receptors, T cellmaturation/activation/differentiation, B cell generation/activation/differentiation Cytokines, Complement system, cell Immune response to infections, Hypersensitivity reactions, Vaccines, Immuno-deficiency syndromes, Autoimmunity, Transplantation immunology, Cancer and immune system, Immunodiagnostics, Immunotherapy.
13. CLINICAL BIOCHEMISTRY
Basic principles and practice of clinical biochemistry, analytical techniques and instrumentation, clinical correlates and analytical procedures, regulation of fluid and electrolyte balance and associated disorders, regulation of acid-base balance and associated disorders, biochemistry of the endocrine system, hematopoietic disorders, hemostasis and thrombosis, cardiovascular system, respiratory system, kidney, gastrointestinal system, liver, bone and mineral metabolism, nervous system.
14. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
15. MEDICO LEGAL ASPECTS RELEVANT TO THE DISCIPLINE.
16. INDIAN MEDICAL COUNCIL (PROFESSIONAL CONDUCT, ETIQUETTE AND
ETHICS) REGULATIONS, 2002
17. CURRENT TRENDS AND RECENT ADVANCEMENTS IN THE FIELD OF
BIOCHEMISTRY
Professor, Anatomy- Class-I, Associate Professor, Anatomy- Class-I, Assistant Professor, Anatomy- Class-I:
1. GROSS ANATOMY
Gross Anatomy of entire body including upper limb, lower limb, thorax, abdomen,
pelvis, perineum, head and neck, brain and spinal cord
2. Developmental Anatomy/Embryology
General embryology: gametogenesis, fertilization, implantation and placenta, early human embryonic development. Systemic embryology: development of organ systems and associated common congenital abnormalities with teratogenesis, Physiological correlations of congenital anomalies.
3. HISTOLOGY AND HISTOCHEMISTRY
Cell Biology
Cytoplasm – cytoplasmic matrix, cell membrane, cell organelles, cytoskeleton, cell inclusions, cilia and flagella, Nucleus – nuclear envelope, nuclear matrix, DNA and other components of chromatin, protein synthesis, nucleolus, nuclear changes indicating cell death. Cell cycle – mitosis, meiosis, cell renewal. Cellular differentiation and proliferation.
Microscopic structure of the body: Principles of light, transmission and scanning, electron, fluorescent, confocal and virtual microscopy. The systems/organs of body – Cellular organization, light and electron microscopic features, structure – function correlations, and cellular organization
4. NEUROANATOMY
Brain and its environment, Development of the nervous system, Neuron and Neuroglia, Somatic sensory system, Olfactory and optic pathways, Cochleovestibular and gustatory pathways, Motor pathways, Central autonomic pathways, Hypothalamo-hypophyseal system, Limbic system, Basal ganglia, Reticular system, Cross Sectional anatomy of brain and spinal Cord, Detailed structure of the central nervous system and its applied aspect
5. GENETICS
Human Chromosomes – Structure, number and classification, methods of chromosome preparation banding patterns. Chromosome abnormalities, Autosomal and Sex chromosomal abnormalities syndromes, Molecular and Cytogenetics. Single gene pattern inheritance: Autosomal and Sex chromosomal pattern of inheritance, Intermediate pattern and multiple alleles, Mutations, Non Mendelian inheritance, Mitochondrial inheritance, Genome imprinting, parental disomy, Multifactorial pattern of inheritance: Criteria for multifactorial inheritance, Teratology, Structure gene, Molecular Screening, Cancer GeneticsHaematological malignancies, Pharmacogenetics. Reproduction Genetics – Male
and Female Infertility, Abortuses, Assisted reproduction, Preimplantation genetics, Prenatal diagnosis, Genetic Counseling and Ethics of Genetics, Principles of Gene therapy and its applied knowledge
6. IMMUNOLOGY
Immune system and the cell types involved in defense mechanisms of the body. Gross features, cytoarchitecture, functions, development and histogenesis of various primary and secondary lymphoid organs in the body, Biological and clinical significance of the major histocompatibility complex of man including its role in transplantation, disease susceptibility/resistance and genetic control of the immune response., Common techniques employed in cellular immunology and his to compatibility testing, Molecular hybridization and PCR technology in immunology research particularly mechanism of antigen presentation, structural and functional relevance of the T cell receptor, genetic control of the immune response, Molecular basis of susceptibility to disease
7. APPLIED ANATOMY AND RECENT ADVANCES
Clinical correlations of structure and functions of human body. Anatomical basis and explanations for clinical problems, Applications of knowledge of development, structural (microscopy), neuro anatomy to comprehend deviations from normal. Recent advances in medical sciences which facilitate comprehension of structure function correlations and applications in clinical problem solving. Collection, maintenance and application of stem cells, cryobanking and principles of organ donation from recently dead bodies
8. SURFACE MARKING AND RADIOLOGY
Surface marking of all regions of the body. Interpretation of normal radiographs of the body including special contrast procedures including barium studies, cholicystrography, pylography, salphingography. Normal CT Scan, MRI and Ultrasound.
- Anthropology
Different anthropological traits, Identification and use of Anthropological instruments.
- Forensic Medicine:
Identification of human bones from their remains and determination of sex, Age
and height. for medico legal application of Anatomy.
9. OUTLINE OF COMPARATIVE ANATOMY OF THE WHOLE BODY AND
BASIC HUMAN EVOLUTION
10.RESEARCH METHODOLOGY.
11.MEDICO LEGAL ASPECTS RELEVANT TO THE DISCIPLINE.
12.INDIAN MEDICAL COUNCIL (PROFESSIONAL CONDUCT, ETIQUETTE
AND ETHICS) REGULATIONS, 2002.
13.CURRENT TRENDS AND RECENT ADVANCEMENTS IN THE FILED OF
ANATOMY.

