Samsung’s 2nm Process Technology: Ever since the Snapdragon 8 Gen 1 incident, Qualcomm has largely turned to TSMC for chip manufacturing. However, recent reports suggest a possible return to Samsung Foundry for the fabrication of future flagship Snapdragon processors, potentially utilizing Samsung’s cutting-edge 2nm (SF2) process.
Qualcomm’s Strategy Shift: A Move Towards Samsung Foundry?
Starting with the Snapdragon 8+ Gen 1 chips, Qualcomm has shifted its focus to TSMC. Nevertheless, there are indications that the company may consider Samsung Foundry for its flagship Snapdragon chips, with the upcoming Snapdragon 8 Gen 5 potentially using Samsung’s 2nm process technology.
Semiconductor Industry Landscape: A $500 Billion Market
The global semiconductor chip fabrication segment exceeded $500 billion last year, driving fierce competition among chip fabricators. As companies race to develop 2nm and 3nm technologies, being the first to market with new advancements positions them to secure orders from major clients like AMD, Apple, MediaTek, Nvidia, and Qualcomm.
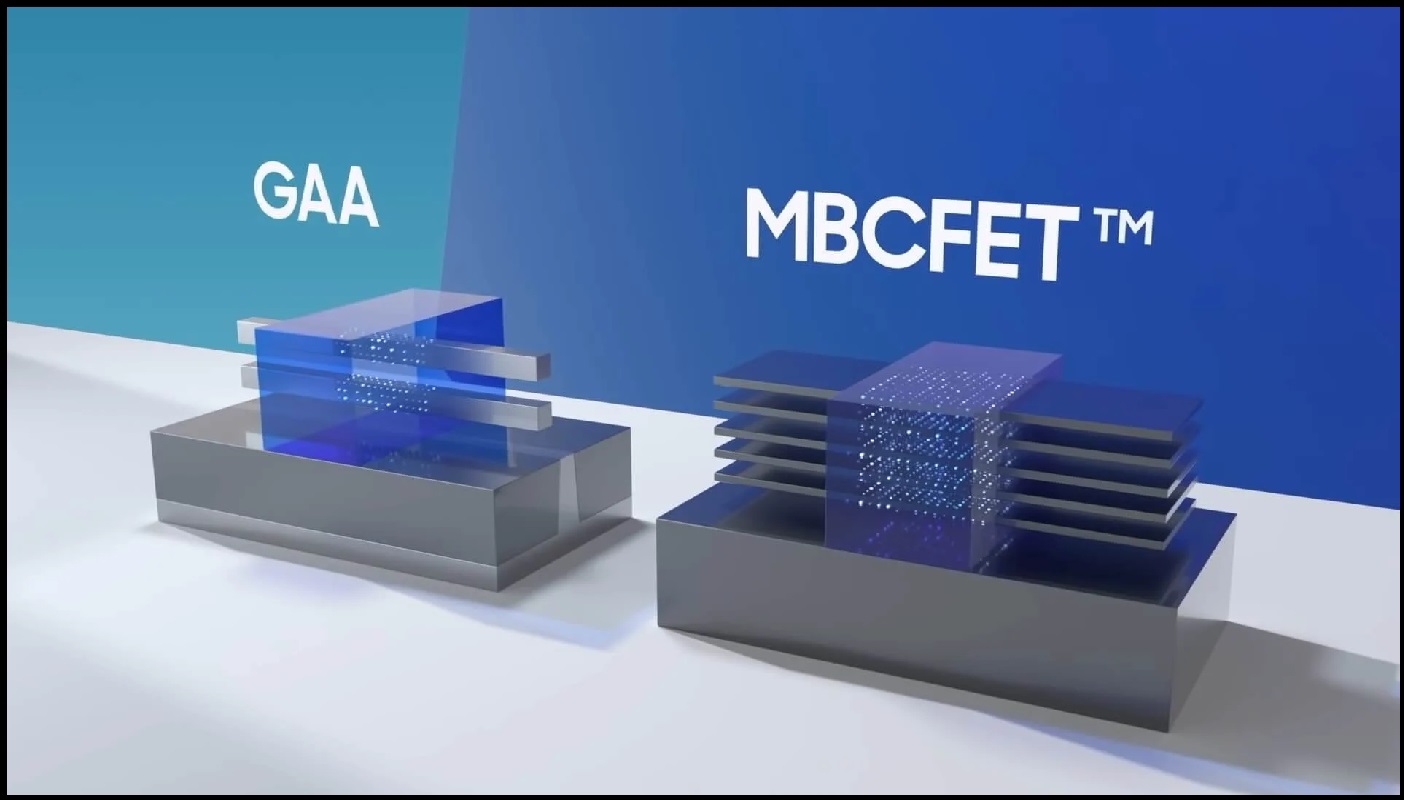
Samsung’s Competitive Edge: 2nm Technology and Client Strategies
Samsung, having been the first to produce 3nm chips and introduce the MBCFET design, believes its transition to 2nm will be smoother than its competitors. As the second sourcing hub, Samsung Foundry offers cut-price versions of its 2nm technology to attract clients like Nvidia, challenging TSMC’s dominance. Doubts persist regarding Samsung’s ability to achieve high yields for complex chips, but the company insists on its improved yield rates.
Industry Race to Mass Production: 2nm Chips by 2025
TSMC and Samsung Foundry both claim readiness for mass production of 2nm chips by 2025. Intel Foundry Services (IFS) aims to start mass production of 18A (1.8nm class) chips by the end of 2024. Despite these ambitious timelines, doubts linger over the performance gains of smaller chips, with experts suggesting diminishing returns. Samsung Foundry sees an opportunity to narrow the gap with TSMC, its primary rival, through advancements in 2nm and 3nm chip technologies.
Challenges and Opportunities for Samsung Foundry: Yield Rates and Diversification
While Samsung Foundry asserts improved yield rates, insiders remain skeptical, citing a mere 60% yield for simpler chips using the 3nm process. Concerns about design leaks between divisions may persist, but customer interest in diversifying the supply chain could provide Samsung Foundry with opportunities in the years ahead.
In Conclusion, As Qualcomm contemplates its chip manufacturing strategy, the dynamic semiconductor industry landscape continues to witness intense competition. The potential collaboration between Qualcomm and Samsung Foundry for flagship Snapdragon chips underscores the ever-evolving nature of technology alliances and the pursuit of cutting-edge semiconductor processes.

