TNPSC Road Inspector Syllabus 2023 (Released) Check Exam Pattern Here: The Tamil Nadu Public Service Commission released the TNPSC Road Inspector Exam Syllabus 2023. The officials of TNPSC going to conduct the Tamil Nadu Road Inspector Exam 2023. As per the TNPSC’s Latest Information, the authorities going to hold the TN Road Inspector Exam 2023 on 07.05.2023. Those eligible candidates who were waiting for TN Road Inspector Syllabus 2023 or TNPSC Road Inspector Exam Pattern 2023 can download the TN Road Inspector Syllabus 2023, Tamilnadu Road Inspector Syllabus from the official website @ tnpsc.gov.in. For the sake of Aspirants, we had given a Tamilnadu Road Inspector Syllabus 2023 given this article.

tnpsc.gov.in Road Inspector Syllabus 2023 – Details
| TNPSC Road Inspector Exam Pattern 2023 Download | |
| Board Name | Tamil Nadu Public Service Commission (TNPSC) |
| Exam Name | Road Inspector |
| Exam Date | 07.05.2023 |
| Category | Syllabus |
| Syllabus Status | Available Now |
| State | Tamil Nadu (TN) |
| Official site | tnpsc.gov.in |
Tamil Nadu Road Inspector Exam Pattern 2023 – Overview
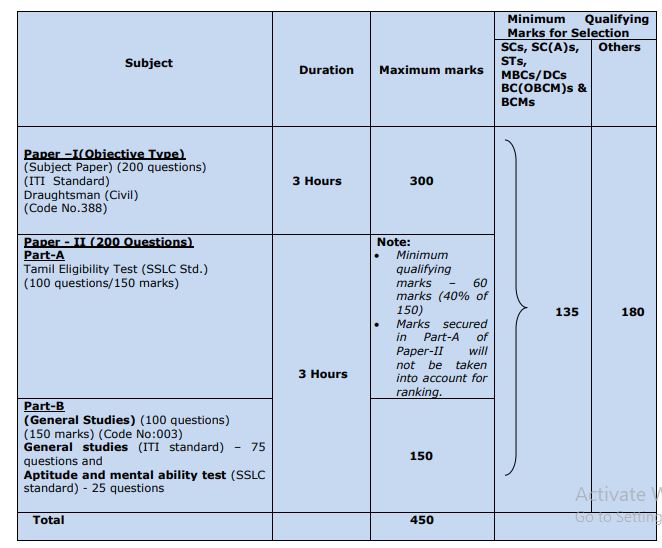
TN Road Inspector Exam Date & Time 2023
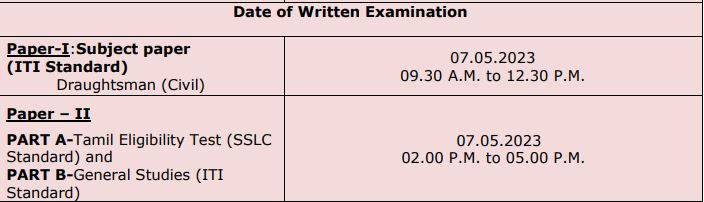
TN Road Inspector Syllabus 2023 – Full Details
DRAUGHTSMAN (CIVIL) (ITI STANDARD)
UNIT 1: BASIC ENGINEERING DRAWING
Engineering Drawing:
State the importance of engineering drawing, State the areas of civil engineering drawing.
List of drawing instruments, equipment, and materials to be used during training:
State instruments, equipment, and materials List out instruments, equipment, and materials, State the standard as per 962-1987, To use different drawing instruments, equipment, and materials, and Follow precautions in the use of instruments, equipment, and materials.
Layout of drawing Sheet:
State the system of the layout of a drawing sheet, List the different layout for the designated drawing sheet explains the title block.
Folding of drawing Sheet:
State the purpose of folding a drawing sheet, Explain the method of folding for drawing sheet
UNIT 2: GEOMETRICAL CONSTRUCTION:
Plane Geometrical construction:
Define the terms of most commonly used geometrical shapes
Types of Lines and Angles:
Define points and lines, State the classification of lines, State the different types of angles, and Explain the method of measuring angles.
Triangles and their types:
Define triangles, Name the different types of triangles and state their properties.
Quadrilaterals and their properties:
Define a quadrilateral, Name the quadrilaterals, State the properties of quadrilaterals
Polygon and their properties:
Define Polygon, Name the Polygon in terms of the number of sides, and State the properties of the polygon.
UNIT 3: CHAIN SURVEYING
Introduction – History and principles of chain survey and instrument & employed
Define surveying, Explain the classification of Surveying, Narrate different methods of measurements, and Express the instruments used for chain surveying.
Introduction about chain survey instruments
State the construction and uses of the chain survey instruments
Testing of metric chain (20m/30m)
State the necessity of checking the chain, State the methods of testing, List out the errors in the chain, State the limits of error in the chain, Explain the adjust the chain, State Indian optical square
Measurement of distance by chain and chaining
State chaining and chaining a line, State unfolding the chain, Describe the reading of the chain, State folding the chain, Calculate the errors in chaining
UNIT 4: COMPASS SURVEYING
Identification and parts of instruments in compass survey:
State about traversing, State types of compass, Name the prismatic compass and construction, Construction of survey’s compass
Determining the bearing of a given triangular plot of ABC and calculation of included angles:
Calculate angles from bearing, Calculate bearing from angles
Determining the bearing of a given pentagonal plot of ABCDE and calculation of included angles
Calculate angles from bearings for a closed traverse, Calculate bearing from angles for a closed traverse, Calculate the bearing of a pentagon
Magnetic declination and local attraction
Define the dip of the Magnetic needles, State the magnetic declination and variations, Calculate true Bearing, State local attraction, and its elimination, Explain errors and limits, State the testing of the prismatic compass
UNIT 5: PLANE TABLE SURVEYING
Instrument used in plane table surveying:
State plane tabling, Name the instruments and accessories used in plan tabling, State the construction and uses of instruments and accessories used in plan tabling, Explain leveling, centering, and orientation in plain tabling, Explain the methods of plain tabling
Resection method of plane table survey:
State the resection method of plane table survey
UNIT 6: LEVELLING
Types of leveling:
Name the various types of leveling, Explain simple leveling, Explain differential leveling, and Complete the reduced levels of points.
UNIT 7: ROAD ENGINEERING – I:
Introduction to road engineering:
Define road, Define highway engineering, Define necessity and characteristics of road
Technical term used in road engineering:
Define road and Total Station advantage, Define various terms used in road engineering, Describe the various advantages of road
Principle of road alignment:
Alignment of road, Express the principle of highway alignment, Explain the different surveys required for alignment
Classification of roads:
Describe the different classifications of roads
UNIT 8: ROAD ENGINEERING II:
Road Margins:
Define road margin, Describe the element Total Station of road margin
Camber, superelevation, sight distance, and gradient:
Define camber, Explain super elevation, sight distance, and express gradient
UNIT 9: TOTAL STATION
Introduction to the total station:
Get introduced to Total station, Learn the evaluation of Total station from the convectional equipment Total Station, Explain the benefits Total Station and uses of Total station
Types of total station:
Explain the advantages and disadvantages of Total station, Explain the types of Total Station, Explain the precautions to be taken while using Total Station
Measurement with total station:
Explain the equipment required for Total Station surveying, Explain the procedure of measurement with Total Station
Characteristics and features of total station:
Define the features of Total Station, State the characteristics of Total Station, Advantages and disadvantages of Total Station
Principle of EDM- Working needs setting and measurement Total Station:
Define EDM, State the principle of EDM, and Features of EDM
Setting and measurement Total Station:
Define distance measuring, State principal of EDM, State classification of EDM
Total station Prism- instrument error operation:
Explain Total Station prisms, Describe sources of error in EDM, EDM instrument operation, Uses of EDM
Electronic display and data recording:
Define electronic data recording, Explain field computers, Define recording module, Internal memories
Rectangular and Polar Co-ordinate system:
Illustrate rectangular and polar coordinates
UNIT 10: GLOBAL POSITIONING SYSTEM
Introduction of GPS:
Explain the GPS coordinate system, Describe Geographic latitude and longitude, GPS equipment
Satellite and Conventional Geodetic system:
What is a satellite system, Define a Geodetic system
GPS coordinate system and component Total Station of GPS & System segment Total Station:
Explain GPS coordinate system, Describe Geographic Latitude and Longitude, Explain and describe component Total Station GPS receiver
GPS segment Total Station:
Define GPS segment
Principle of Operation of GPS and surveying with GPS:
State the Principle of Operation of GPS, Describe the role of transit in GPS
Remote sensing:
Explain Remote sensing, Distinguish between GPS, GIS and Total Station
GPS signal code – GPS basics:
Introduction to digital signal, Explain data acquisition system, Describe signal processing, Explain code an basics


Paper II
1. GENERAL SCIENCE
i. Nature of Universe – Measurement of Physical Quantities – General Scientific Laws in Motion – Force, Pressure and Energy – Everyday application of the basic principles of Mechanics, Electricity, Magnetism, Light, Sound, Heat and Nuclear Physics in our daily life.
ii. Elements and Compounds, Acids, Bases, Salts, Petroleum Products, Fertilizers, Pesticides, Metallurgy and Food Adulterants.
iii. Main concepts of Life Science, Classification of living organisms, Evolution, Genetics, Physiology, Nutrition, Health and Hygiene, and Human diseases.
iv. Environmental Science.
2. CURRENT EVENTS
i. Latest diary of events – National symbols–Profile of states –Eminent personalities and places in the news–Sports –Books and Authors.
ii. Welfare Scheme of Government – Political parties and Political system in Tamil Nadu and India.
iii. Latest inventions in Science and Technology – Geographical Land Marks –
Current Socio–Economic issues.
3. GEOGRAPHY
i. Earth Location – Physical Features – Monsoon, rainfall, weather, and climate– Water resources–Rivers –Soil, Minerals, and Natural resources– Forest and Wildlife–Agriculture pattern.
ii. Transport– Communication.
iii. Population density and distribution in Tamil Nadu and India.
iv. Calamities–Disaster Management–Environment – Climate change.
4. HISTORY AND CULTURE OF INDIA
i. Indus Valley Civilization –Guptas, Delhi Sultans, Mughals, and Marathas – South Indian History.
ii. Characteristics of Indian Culture, Unity in Diversity–Race, Language, Custom.
iii. India as a Secular State.
5. INDIAN POLITY
i. Constitution of India–Preamble to the Constitution–Salient features of the Constitution–Union, State and Union Territory.
ii. Citizenship, Fundamental Rights, Fundamental Duties, Directive Principles of State Policy.
iii. Union Executive, Union Legislature–State Executive, State Legislature– Local Governments, Panchayat Raj.
iv. Spirit of Federalism: Centre-State Relationships.
v. Election–Judiciary in India–Rule of Law.
vi. Corruption in public life – Anti-Corruption measures – Lokpal and Lokayukta – Right to Information – Empowerment of Women – Consumer Protection Forums – Human Rights Charter.
6. INDIAN ECONOMY
i. Nature of Indian economy–Five-year plan models – an assessment – Planning Commission and NITI Aayog.
ii. Sources of revenue–Reserve Bank of India – Finance Commission– Resource sharing between Union and State Governments –Goods and Services Tax.
iii. Economic Trends – Employment Generation, Land Reforms, and Agriculture – Application of Science and Technology in Agriculture – Industrial growth – Rural Welfare oriented programs – Social Problems –Population, Education, Health, Employment, Poverty.
7. INDIAN NATIONAL MOVEMENT
i. National Renaissance –Early uprising against British Rule–Indian National Congress – Emergence of Leaders –B.R.Ambedkar, Bhagat Singh, Bharathiar, V.O.Chidambaranar, ThanthaiPeriyar, Jawaharlal Nehru, Rabindranath Tagore, Kamarajar, Mahatma Gandhi, Maulana AbulKalam Azad, Rajaji, Subhash Chandra Bose, Muthulaksmi Ammaiyar, Muvalur Ramamirtham, and other National Leaders.
ii. Different modes of Agitation of Tamil Nadu and movements.
8. HISTORY, CULTURE, HERITAGE, AND SOCIO-POLITICAL MOVEMENTS OF TAMIL NADU
i. History of Tamil Society, related Archaeological Discoveries, Tamil Literature from Sangam age till contemporary times.
ii. Thirukkural:
a) Significance as a Secular Literature.
b) Relevance to Everyday Life.
c) Impact of Thirukkural on Humanity.
d) Thirukkural and Universal Values – Equality, Humanism, etc.
e) Relevance to Socio–Politico–Economic affairs.
f) Philosophical content in Thirukkural.
iii. Role of Tamil Nadu in freedom struggle – Early agitations against British Rule – Role of women in the freedom struggle.
iv. Various Social reformers, Social reform movements and
Social transformation of Tamil Nadu.
9. DEVELOPMENT ADMINISTRATION IN TAMIL NADU
i. Social Justice and Social Harmony as the Cornerstones of Socio-Economic Development.
ii. Education and Health systems in Tamil Nadu.
iii. Geography of Tamil Nadu and its impact on Economic growth.
10. APTITUDE & MENTAL ABILITY TESTS
i. Simplification–Percentage–Highest Common Factor(HCF)– Lowest Common Multiple(LCM).
ii. Ratio and Proportion.
iii. Simple Interest– Compound Interest–Area–Volume–Time and Work.
iv. Logical Reasoning – Puzzles – Dice–Visual Reasoning–Alpha Numeric Reasoning– Number Series.

